cosmos.wikisort.org - Raumschiff
Der Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE), auch als Explorer 97 oder SMEX 14 bekannt, ist ein Weltraumteleskop, das in Zusammenarbeit von Agenzia Spaziale Italiana und NASA konstruiert wurde. Es besteht aus drei Teleskopen, welche die Polarisation der kosmischen Röntgenstrahlung messen sollen.[1]
| Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer | |
|---|---|
 | |
| IXPE-Satellit, oben sind seine drei identischen Röntgenoptikelemente, unten die Sensoren | |
| Typ: | Weltraumteleskop |
| Land: | |
| Betreiber: | |
| COSPAR-ID: | 2021-121A |
| Missionsdaten | |
| Masse: | 330 kg |
| Start: | 9. Dezember 2021, 06:00 UTC |
| Startplatz: | Kennedy Space Center, LC-39A |
| Trägerrakete: | Falcon 9 Block 5 |
| Status: | im Orbit, aktiv |
| Bahndaten | |
| Umlaufzeit: | 90 min |
| Bahnneigung: | 0,20° |
| Apogäumshöhe: | 540 km |
| Perigäumshöhe: | 540 km |
Die Hauptziele der Mission werden aktive galaktische Kerne, Mikroquasare, Pulsare, Pulsarwind-Nebel, Magnetare, Röntgendoppelsterne, Supernova-Überreste und das galaktische Zentrum sein.[2]
Mission
Das IXPE wird wichtige neue Informationen zur Geometrie und die physikalischen Prozesse bei der Strahlungsemission und Beschleunigung von Partikeln in Umgebungen mit extremen Magnetfeldern und Gravitationsfeldern liefern.
Der Start erfolgte am 9. Dezember 2021 vom Kennedy Space Center an Bord einer Falcon-9-Rakete in einen Low-Earth-Orbit.[3]
Galerie
 Aufbau des Teleskops
Aufbau des Teleskops- Vor dem Start
- IXPE wird in die Nutzlastverkleidung integriert
- Die Falcon-9-Rakete auf der Startrampe
- Start der Falcon-9-Rakete mit IXPE
- IXPE löst sich von der Raketenoberstufe
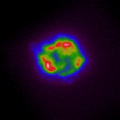 Aufnahme der Überreste der Supernova Cassiopeia A
Aufnahme der Überreste der Supernova Cassiopeia A
Weblinks
- Beitrag des MDR vor dem Start (abgerufen 10. September 2022)
- Informationen zu den ersten Beobachtungen von astropage.eu (16. Februar 2022, abgerufen 10. September 2022)
Einzelnachweise
- IXPE: Home. Abgerufen am 5. September 2022.
- Karen Northon: NASA Selects Mission to Study Black Holes, Cosmic X-ray Mysteries. 3. Januar 2017, abgerufen am 5. September 2022.
- Steven R. Ehlert, Riccardo Ferrazzoli, Andrea Marinucci, Herman L. Marshall, Riccardo Middei: Limits on X-Ray Polarization at the Core of Centaurus A as Observed with the Imaging X-Ray Polarimetry Explorer. In: The Astrophysical Journal. Band 935, Nr. 2, 1. August 2022, ISSN 0004-637X, S. 116, doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac8056 (iop.org [abgerufen am 5. September 2022]).
На других языках
- [de] Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer
[en] IXPE
Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer, commonly known as IXPE or SMEX-14, is a space observatory with three identical telescopes designed to measure the polarization of cosmic X-rays of black holes, neutron stars, and pulsars.[6] The observatory, which was launched on 9 December 2021, is an international collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency (ASI). It is part of NASA's Explorers program, which designs low-cost spacecraft to study heliophysics and astrophysics.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии






