cosmos.wikisort.org - Spacecraft
XSS-10 (eXperimental Small Satellite 10) was a small, low-cost micro-spacecraft developed by the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory's Space Vehicles Directorate to test technology for line-of-sight guidance of spacecraft.[2] The project was initiated at AFRL by Program Manager David Barnhart[3] and completed by Georgia Tech Research Institute engineer Thom Davis and team.[4] The project was declared a success shortly after launch.[5]

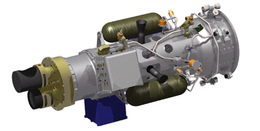 XSS-10 computer model | |
| Mission type | Technology |
|---|---|
| Operator | AFRL |
| COSPAR ID | 2003-005B |
| SATCAT no. | 27664 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | Boeing |
| Launch mass | 28 kilograms (62 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | January 29, 2003, 18:06:00 UTC |
| Rocket | Delta II 7925-9.5 |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral SLC-17B |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.020384971 |
| Perigee altitude | 518.0 kilometers (321.9 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 805.0 kilometers (500.2 mi) |
| Inclination | 39.75 degrees |
| Period | 98.0 minutes |
| Epoch | 29 January 2003, 13:06:00 UTC[1] |
References
- "NASA - NSSDCA - Spacecraft - Trajectory Details". nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. Retrieved 2018-05-02.
- Banke, Jim (2003-01-30). "Air Force XSS-10 Micro-Satellite Mission a Success". Space.com. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved 2008-07-28.
- David A. Barnhart et al, “XSS-10 Micro-satellite Demonstration,” AIAA-1998-5298, AIAA Defense and Civil Space Programs Conference and Exhibit, Huntsville, AL, Oct. 28-30, 1998
- "Big plans for small satellites". Historical archive. Georgia Tech Research Institute. Retrieved 2012-10-26.
- Sanders, Jane M (2003-08-11). "The Little Engine That Could". Research Horizons. Georgia Institute of Technology. Retrieved 2012-10-26.
External links
- XSS Micro-Satellite at Boeing.com
На других языках
[de] XSS 10
XSS 10 (Experimental Satellite System 10) war ein kleiner, militärischer Experimentalsatellit, der vom Air Force Research Laboratory der United States Air Force entwickelt wurde, um Annäherungsoperationen an andere Raumflugkörper zu erproben.- [en] XSS-10
Текст в блоке "Читать" взят с сайта "Википедия" и доступен по лицензии Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike; в отдельных случаях могут действовать дополнительные условия.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
2019-2025
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии