cosmos.wikisort.org - Spacecraft
The Solar Mesosphere Explorer (also known as Explorer 64) was a NASA spacecraft to investigate the processes that create and destroy ozone in Earth's upper of the atmosphere of Earth. The mesosphere is a layer of the atmosphere extending from the top of the stratosphere to an altitude of about 80 km (50 mi). The spacecraft carried five instruments to measure ozone, water vapor, and incoming solar radiation.[1]
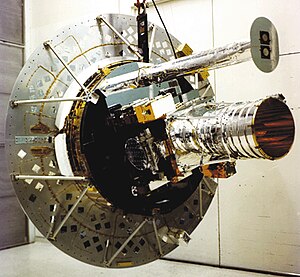 Solar Mesosphere Explorer (Explorer 64) satellite | |
| Names | Explorer 64 Solar Mesosphere Explorer |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Earth observation |
| Operator | NASA / LASP |
| COSPAR ID | 1981-100A |
| SATCAT no. | 12887 |
| Mission duration | 7.5 years (achieved) |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Explorer LXIV |
| Spacecraft type | Solar Mesosphere Explorer |
| Bus | SME |
| Manufacturer | Ball Space Systems |
| Launch mass | 437 kg (963 lb) |
| Dimensions | Cylinder: 1.25 m (4 ft 1 in) diameter by 1.7 m (5 ft 7 in) high |
| Power | Solar panels and nickel-cadmiumd batteries |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 6 October 1981, 11:27 UTC |
| Rocket | Thor-Delta 2310 (Thor 639 / Delta 157) |
| Launch site | Vandenberg, SLC-2W |
| Contractor | Douglas Aircraft Company |
| Entered service | 6 October 1981 |
| End of mission | |
| Deactivated | 31 December 1988 |
| Last contact | 4 April 1989 |
| Decay date | 5 March 1991 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 535 km (332 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 551 km (342 mi) |
| Inclination | 97.56° |
| Period | 95.50 minutes |
| Instruments | |
| Ultraviolet ozone spectrometer Micrometer spectrometer Nitrogen dioxide spectrometer Four-channel infrared radiometer Solar ultraviolet monitor Solar proton alarm detector | |
Explorer Program | |
Mission
Explorer 64 studied the processes that create and destroy ozone in the Earth's mesosphere. Over its 7.5 years mission, SME measured ultraviolet solar flux, ozone density, and the density of other molecules important to the understanding of ozone chemistry. During the mission over one hundred undergraduate and graduate students were involved in nearly every aspect of SME operations, including planning and scheduling spacecraft and science activities, controlling the spacecraft and its ground support system, and analyzing spacecraft subsystem performance.[2]
Spacecraft
Managed for NASA by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the Solar Mesosphere Explorer was built by Ball Space Systems and operated by the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics of the University of Colorado Boulder.[2]
Characteristics:[1]
- Mass: 437 kilograms
- Power: Solar panels and nickel-cadmium batteries
- Configuration: Cylinder 1.25 meter diameter by 1.7 meter high
- Science instruments: Ultraviolet ozone spectrometer, Micrometre spectrometer, Nitrogen dioxide spectrometer, Four-channel infrared radiometer, Solar ultraviolet monitor, Solar proton alarm detector
Launch
Launched on 6 October 1981, on a Thor-Delta 2310 from Vandenberg Air Force Base, in California, the satellite returned data until 4 April 1989.[1]
Atmospheric entry
The spacecraft reentered Earth's atmosphere on 5 March 1991.[1]
See also
Explorer program
References
- "Past Missions - Solar Mesosphere Explorer". Archived from the original on 12 July 2007. Retrieved 23 November 2021.
- "Solar Mesosphere Explorer - Quick facts". Archived from the original on 13 July 2007. Retrieved 23 November 2021.
External links
- JPL - Solar Mesosphere Explorer
- Launch video
- Nitric oxide measurements results
- Daily Solar Irradiance results
На других языках
[de] Solar Mesosphere Explorer
Der Solar Mesosphere Explorer (SME) bzw. Explorer 64 war ein Forschungssatellit der NASA, der die ozonerzeugenden und -zerstörenden Prozesse in der Mesosphäre und oberen Stratosphäre der Erde und den Einfluss der Sonneneinstrahlung auf diese Prozesse erforscht hat. Der Satellit wurde am 6. Oktober 1981 von Vandenberg mit einer Delta-2310-Rakete gestartet. Nach dem Start trat SME in eine sonnensynchrone niedrige Erdumlaufbahn ein. Er war spinstabilisiert mit 5 Umdrehungen in der Minute.- [en] Solar Mesosphere Explorer
[es] Explorer 64
Explorer 64, bautizado como Solar Mesosphere Explorer o SME, fue un satélite artificial de la NASA lanzado el 6 de octubre de 1981 mediante un cohete Delta desde la base de Vandenberg a una órbita heliosincrónica.[ru] Solar Mesosphere Explorer
Solar Mesosphere Explorer— американский искусственный спутник Земли, созданный для изучения озонового слоя и запущенный 6 октября 1981 года с авиабазы Ванденберг ракетой-носителем Дельта 2310 639/D157.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
