cosmos.wikisort.org - Spacecraft
OSO 3 (Orbiting Solar Observatory 3), or Third Orbiting Solar Observatory[2][3] (known as OSO E2 before launch) was launched on March 8, 1967, into a nearly circular orbit of mean altitude 550 km, inclined at 33° to the equatorial plane. Its on-board tape recorder failed on June 28, 1968, allowing only the acquisition of sparse real-time data during station passes thereafter; the last data were received on November 10, 1969. OSO 3 reentered the Earth's atmosphere and burned up on April 4, 1982.
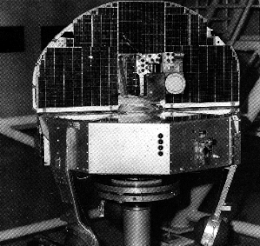 The third Orbiting Solar Observatory, OSO 3, showing its "Sail" (upper), carrying solar experiments pointed at the Sun, and its rotating "Wheel" (lower), carrying two sky-scanning survey instruments: the UCSD hard X-ray experiment, and the MIT gamma-ray telescope | |
| Mission type | Solar physics |
|---|---|
| Operator | NASA |
| COSPAR ID | 1967-020A |
| SATCAT no. | 02703 |
| Mission duration | 2 years, 8 months |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | BBRC |
| Launch mass | 281 kilograms (619 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | March 8, 1967, 16:19:00 UTC |
| Rocket | Delta C |
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral LC-17A |
| End of mission | |
| Last contact | November 10, 1969 |
| Decay date | April 4, 1982 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.002164 |
| Perigee altitude | 534 kilometers (332 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 564 kilometers (350 mi) |
| Inclination | 32.87 degrees |
| Period | 95.53 minutes |
| Mean motion | 15.07 |
| Epoch | May 8, 1967, 11:19:00 UTC[1] |
Like all the American Orbiting Solar Observatory (OSO) series satellites, it had two major segments: one, the "Sail", was stabilized to face the Sun, and carried both solar panels and Sun-pointing experiments for solar physics. The other, "Wheel" section, rotated to provide overall gyroscopic stability and also carried sky scanning instruments that swept the sky as the wheel turned, approximately every 2 seconds.
Instrumentation
| Name | Target | Principal Investigator |
|---|---|---|
| High Energy Gamma Ray (> 50 MeV) | anti-solar | Kraushaar, W. L., Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
| Cosmic Ray Spectrum Detector and Gamma Ray Analyzer | Sun, all-sky | Kaplon, Morton F, University of Rochester |
| Directional Radiometer Experiment | Earth | Neel, Carr B Jr, NASA Ames Research Center |
| Earth Albedo (0.32- to 0.78-µm) | Earth | Neel, Carr B Jr, NASA Ames Research Center |
| Solar EUV Spectrometer 0.1 to 40.0 nm | Sun | Neupert, Werner M, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center |
| 0.8- to 1.2-nm Solar X-Ray Ion Chamber | Sun | Teske, Richard G, University of Michigan |
| Solar and Celestial Gamma-Ray Telescope (7.7 to 200 keV) | Sun, all-sky | Laurence E. Peterson University of California, San Diego |
| Thermal Radiation Emissivity | near-Earth space environment | Neel, Carr B Jr, NASA Ames Research Center |
| Extreme Ultraviolet Spectrometer | Sun | Hinteregger, Hans E, Phillips Laboratory |
The Sail carried a hard X-ray experiment from UCSD, with a single thin NaI(Tl) scintillation crystal plus phototube enclosed in a howitzer-shaped CsI(Tl) anti-coincidence shield. The energy resolution was 45% at 30 keV. The instrument operated from 7.7 to 210 keV with 6 channels. The Principal Investigator (PI) was Prof. Laurence E. Peterson of UCSD. Also in the wheel was a cosmic gamma-ray (>50 MeV) sky survey instrument contributed by MIT, with PI Prof. William L. Kraushaar.
Scientific results
OSO-3 obtained extensive hard X-ray observations of solar flares, the cosmic diffuse X-ray background, and multiple observations of Scorpius X-1, the first observation of an extrasolar X-ray source by an observatory satellite.[4][5][6][7]
The MIT gamma-ray instrument obtained the first identification of high-energy cosmic gamma rays emanating from both galactic and extra-galactic sources.[8]
See also
- Orbiting Solar Observatory
- X-ray astronomy
References
- "NASA - NSSDCA - Spacecraft - Trajectory Details". nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov. Retrieved May 2, 2018.
- NASA GSFC X-ray Astronomy Satellites and Missions
- GSFC HEASARC "The Third Orbiting Solar Observatory (OSO-3)"
- Peterson, Laurence E.; Jacobson, Allan S.; Pelling, R. M. (January 24, 1966). "Spectrum of Crab Nebula X Rays to 120 keV". Physical Review Letters. American Physical Society (APS). 16 (4): 142–144. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.16.142. hdl:2060/19660015394. ISSN 0031-9007.
- Peterson, Laurence E.; Jacobson, Allan S. (1966). "The Spectrum of Scorpius XR-1 to 50 KEV". The Astrophysical Journal. American Astronomical Society. 145: 962. Bibcode:1966ApJ...145..962P. doi:10.1086/148848. ISSN 0004-637X.
- Hudson, Hugh S.; Peterson, Laurence E.; Schwartz, Daniel A. (1970). "Simultaneous X-Ray and Optical Observations of SCO X-1 Flares". The Astrophysical Journal. American Astronomical Society. 159: L51. Bibcode:1970ApJ...159L..51H. doi:10.1086/180476. ISSN 0004-637X.
- Pelling, R. M. 1971, Ph.D. dissertation thesis, University of California at San Diego
- Kraushaar, W. L.; Clark, G. W.; Garmire, G. P.; Borken, R.; Higbie, P.; Leong, V.; Thorsos, T. (1972). "High-Energy Cosmic Gamma-Ray Observations from the OSO-3 Satellite". The Astrophysical Journal. American Astronomical Society. 177: 341-363. Bibcode:1972ApJ...177..341K. doi:10.1086/151713. ISSN 0004-637X.
External links
The content of this article was adapted and expanded from NASA's HEASARC: Observatories OSO 3 and NASA's National Space Science Data Center: OSO 3 (Public Domain)
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии