cosmos.wikisort.org - Spacecraft
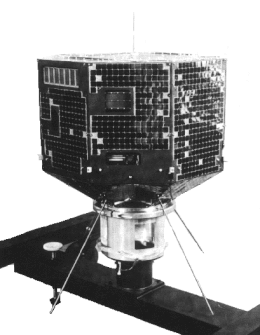
Hakucho (also known as CORSA-b before launch; CORSA stands for Cosmic Radiation Satellite) was Japan's first X-ray astronomy satellite, developed by the Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science (then a division of the University of Tokyo). It was launched from the Kagoshima Space Center by the ISAS M-3C rocket on the M-3C-4 mission on February 21, 1979 [1] and reentered the atmosphere on April 15, 1985.[2]
 | |
| Mission type | X Ray Celestial Observation |
|---|---|
| Operator | Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (Japan) |
| COSPAR ID | 1979-014A |
| SATCAT no. | 11272 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Launch mass | 96.0 kilograms (211.6 lb) |
| Dimensions | ⌀760mm×650mm |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 21 February 1979 UTC |
| Rocket | M-3C-Rocket (mission 4) |
| Launch site | Uchinoura Space Center, Kagoshima Prefecture, Japan |
| End of mission | |
| Decay date | April 15, 1985 |
Hakucho was a replacement for the CORSA satellite which failed to launch due to rocket failure on February 4, 1976.[3]
Highlights
- Discovery of soft X-ray transient Cen X-4 and Aql X-1
- Discovery of many burst sources
- Long-term monitoring of X-ray pulsar (e.g. Vela X-1)
- Discovery of 2 Hz variability in the Rapid Burster later named Quasi Period Oscillation.
See also
- Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes
References
- "Hakucho", JAKA Institute of Space and Astronautical Science
- "CelesTrak: Search Satellite Catalog". celestrak.com. Retrieved Nov 28, 2020.
- "Corsa A, B (Hakucho)". Gunter's Space Page. Retrieved Nov 28, 2020.
На других языках
[de] Hakuchō
Hakuchō (japanisch はくちょう, „Schwan“) war der erste japanische Satellit für Röntgenastronomie. Der ursprüngliche Name des Projekts bis zum Start war CORSA-B (Cosmic Radiation Satellite B).- [en] Hakucho
[ru] Хакутё
Хакутё (яп. はくちょう Хакутё:, Лебедь, до запуска обозначался яп. 第4号科学衛星CORSA-b, Дай-ён-го кагаку эйсэй CORSA-b — «Четвёртый научный спутник CORSA-b») — японская орбитальная обсерватория, предназначенная для исследования неба в рентгеновских лучах. Разработана и создана в Институте космических исследований и аэронавтики (яп. 宇宙航空研究所 (ISAS)) проектной группой под руководством Минору Ода. Запущена 21 февраля 1979 японской ракетой-носителем M-3C с космического центра Утиноура (Япония). Изначальное название спутника — Corsa-B — отражало то, что спутник является копией спутника Corsa, чей запуск 4 февраля 1976 года был неудачным из-за проблем с ракетой-носителем. После вывода на орбиту спутник был назван «Хакутё» (яп. はくちょう, ромадзи Hakuchō), что в переводе с японского означает «лебедь», по латыни — cygnus. Название спутника представляет собой аллюзию на один из известнейших рентгеновских источников Лебедь X-1 (Cygnus X-1) — двойную систему с компактным объектом. Задачей обсерватории был обзор неба и слежение за вспыхивающими рентгеновскими источниками. Два года обсерватория работала параллельно с обсерваторией HEAO2/Эйнштейн, являясь дополнениям к возможностям этой обсерватории, а с 1983 года работала параллельно со второй японской рентгеновской обсерваторией — Тэмма.Текст в блоке "Читать" взят с сайта "Википедия" и доступен по лицензии Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike; в отдельных случаях могут действовать дополнительные условия.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
2019-2025
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии