cosmos.wikisort.org - Spacecraft
HALCA (Highly Advanced Laboratory for Communications and Astronomy), also known for its project name VSOP (VLBI Space Observatory Programme), the code name MUSES-B (for the second of the Mu Space Engineering Spacecraft series), or just Haruka (はるか)[2] was a Japanese 8 meter diameter radio telescope satellite which was used for Very Long Baseline Interferometry (VLBI). It was the first such space-borne dedicated VLBI mission.
 HALCA after the final assembly during a solar battery check at Uchinoura | |
| Names | MUSES-B VSOP Haruka (はるか) |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Astronomy |
| Operator | ISAS |
| COSPAR ID | 1997-005A |
| SATCAT no. | 24720 |
| Website | HALCA Home |
| Mission duration | 8 years, 9 months, 18 days |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Manufacturer | NEC Toshiba Space Systems |
| Launch mass | 830 kg (1,830 lb) |
| Dimensions | 1.5 m × 1 m (4.9 ft × 3.3 ft) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 04:50, February 12, 1997 (UTC) |
| Rocket | M-5-1 |
| Launch site | Kagoshima M-V Pad |
| End of mission | |
| Disposal | decommissioned |
| Deactivated | November 30, 2005 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Highly elliptical |
| Semi-major axis | 17,259 km (10,724 mi) |
| Eccentricity | 0.5999671 |
| Perigee altitude | 533.5 km (331.5 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 21,244.1 km (13,200.5 mi) |
| Inclination | 31.1880 degrees |
| Period | 376.1 minutes |
| RAAN | 127.6566 degrees |
| Argument of perigee | 143.9533 degrees |
| Mean anomaly | 358.3371 degrees |
| Mean motion | 3.82867831 rev/day |
| Epoch | 28 April 2016, 09:56:58 UTC[1] |
| Revolution no. | 26766 |
| Main telescope | |
| Type | Mesh antenna |
| Diameter | 8 m (26 ft) |
| Wavelengths | 1.3, 6, 18 cm (radio) |
History
It was placed in a highly elliptical orbit with an apogee altitude of 21,400 km and a perigee altitude of 560 km, with an orbital period of approximately 6.3 hours. This orbit allowed imaging of celestial radio sources by the satellite in conjunction with an array of ground-based radio telescopes, such that both good (u,v) plane coverage and very high resolution were obtained.
Although designed to observe in three frequency bands: 1.6 GHz, 5.0 GHz, and 22 GHz, it was found that the sensitivity of the 22 GHz band had severely degraded after orbital deployment, probably caused by vibrational deformation of the dish shape at launch, thus limiting observations to the 1.6 GHz and 5.0 GHz bands.
HALCA was launched in February 1997 from Kagoshima Space Center, and made its final VSOP observations in October 2003, far exceeding its 3-year predicted lifespan, before the loss of attitude control. All operations were officially ended in November 2005.[3]
A follow-up mission ASTRO-G (VSOP-2) was planned, with a proposed launch date of 2012, but the project was eventually cancelled in 2011 due to increasing costs and the difficulties of achieving its science goals. It was expected to achieve resolutions up to ten times higher and up to ten times greater sensitivity than its predecessor HALCA.
The cancellation of ASTRO-G left the Russian Spektr-R mission as the only then operational space VLBI facility.
Antenna
The large 8 meter antenna was designed to unfold in space as the unfolded configuration did not fit inside the rocket fairing. The antenna was a metal mesh of 6000 cables. To form an ideal shape the length of the cables were adjusted on the backside of the antenna. One concern was that the cables could entangle.[4] The deployment of the main reflector started on February 27, 1997. The deployment was done over three hours on the first day and was completed in 20 minutes during the next day.[5]
Highlights
- Observations of hydroxyl masers and pulsars at 1.6 GHz
- Detection of interference fringes for quasar PKS1519-273 between HALCA and terrestrial radio telescopes
- Routines imaging of quasars and radio galaxies etc. by means of experimental VLBI observations with HALCA and terrestrial radio telescope networks
Gallery
- Haruka during a deployment test
- Launch of Haruka on board of a M-V rocket
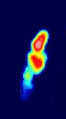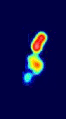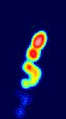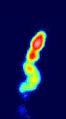 Multi-epoch observations of the quasar VSOP J1927+7358, observed with VSOP between 1997 and 2001
Multi-epoch observations of the quasar VSOP J1927+7358, observed with VSOP between 1997 and 2001 Animation of HALCA around the Earth
Animation of HALCA around the Earth
HALCA · Earth
References
- "HALCA (MUSES-B) Satellite details 1997-005A NORAD 24720". N2YO. 28 April 2016. Retrieved 28 April 2016.
- ""Haruka" large antenna and space VLBI (「はるか」大型アンテナとスペースVLBI)". ISAS JAXA + translate.google.com. Retrieved 2020-01-24.
- "VSOP newsletter number 161".
- "Deployment of 8 m effective aperture antenna (有効口径8mアンテナの開発)". ISAS JAXA + translate.google.com. Retrieved 2020-01-24.
- "Natori's Tears: Successful deployment of large antennas under tension (名取の涙──緊張の中、大型アンテナの展開成功)". ISAS JAXA + translate.google.com. Retrieved 2020-01-24.
External links
На других языках
[de] Highly Advanced Laboratory for Communications and Astronomy
HALCA (jap. .mw-parser-output .Hira{font-size:120%}はるか, Haruka, dt. „weit entfernt“; früher MUSES-B) ist die Abkürzung für Highly Advanced Laboratory for Communications and Astronomy und ist ein japanischer Satellit des Institute of Space and Astronautical Science für VLBI-Beobachtungen. Der Satellit wurde am 12. Februar 1997 mit einer M-V-Rakete vom Kagoshima Space Center in ein elliptisches Erdorbit gestartet. Die Inklination des Orbits beträgt 31,3°, die Höhe des Perigäums 560 km und die des Apogäums 21400 km.- [en] HALCA
[es] Muses B
Haruka (muy lejos, en japonés), denominado inicialmente MUSES-B y también conocido como HALCA (Highly Advanced Laboratory for Communications and Astronomy), fue un observatorio espacial japonés dedicado a la radioastronomía, el primero de su clase en todo el mundo. Fue lanzado el 12 de febrero de 1997 mediante un cohete M-V desde la base de lanzamiento de Kagoshima.[ru] HALCA
HALCA (Highly Advanced Laboratory for Communications and Astronomy), также известен под именем проекта VSOP (VLBI Space Observatory Programme), кодовым названием MUSES-B (для второй серии космических кораблей Mu), или просто Haruka (は る か)[2] — японский космический радиотелескоп диаметром 8 метров, который использовался для интерферометрии с очень длинной базой (VLBI). Это была первая такая космическая миссия VLBI.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии




