cosmos.wikisort.org - SpacecraftSakigake (さきがけ, lit. 'pioneer', 'pathfinder'), known before launch as MS-T5, was Japan's first interplanetary spacecraft, and the first deep space probe to be launched by any country other than the USA or the Soviet Union. It aimed to demonstrate the performance of the new launch vehicle, test its ability to escape from Earth gravity, and observe the interplanetary medium and magnetic field. Sakigake was also supposed to act as a frame of reference for data received from probes that flew closer to Halley's Comet. Early measurements would be used to improve the mission of the Suisei probe launched several months later.
Japanese deep space probe launched in 1985
For the anime, see Cromartie High School.
For the political party, see New Party Sakigake.
Sakigake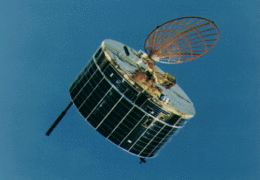 Sakigake spacecraft |
|
| Mission type | Comet flyby |
|---|
| Operator | ISAS |
|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1985-001A  |
|---|
| SATCAT no. | 15464 |
|---|
| Mission duration | 10 years and 10 months (launch date to date of last data transmission) |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Launch mass | 138.1 kilograms (304 lb) |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Launch date | January 7, 1985, 19:27 (1985-01-07UTC19:27Z) UTC |
|---|
| Rocket | Mu-3SII |
|---|
| Launch site | Kagoshima |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Last contact | Data: November 15, 1995 (1995-11-16)
Beacon: January 8, 1999 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Reference system | Heliocentric |
|---|
| Perihelion altitude | 0.92 astronomical units |
|---|
| Aphelion altitude | 1.15 astronomical units |
|---|
| Inclination | 0.07 degrees |
|---|
| Period | 382.8 days |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Closest approach | March 11, 1986, 04:18 UTC |
|---|
| Distance | 6,990,000 kilometres (4,340,000 mi) |
|---|
|
|
| |
Sakigake was developed by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science for the National Space Development Agency (both of which are now part of the Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency, or JAXA). It became a part of the Halley Armada together with Suisei, the Soviet Vega probes, the ESA Giotto and the NASA International Cometary Explorer, to explore Halley's Comet during its 1986 sojourn through the inner Solar System.
Design
Unlike its twin Suisei, it carried no imaging instruments in its instrument payload.
Launch
Sakigake was launched January 7, 1985, from Kagoshima Space Center by M-3SII launch vehicle on M-3SII-1 mission.
Halley encounter
It carried out a flyby of Halley's Comet on March 11, 1986 at a distance of 6.99 million km.
Giacobini-Zinner encounter
There were plans for the spacecraft to go on to an encounter with 21P/Giacobini-Zinner in 1998 but the flyby had to be abandoned due to lack of propellant.
End of mission
Telemetry contact was lost on November 15, 1995, though a beacon signal continued to be received until January 7, 1999.[1][2]
References
External links
 Spaceflight portal
Spaceflight portal
Spacecraft missions to minor planets and comets |
|---|
|
| Active |
- New Horizons (multiple flybys)
- OSIRIS-REx (sample return)
- Hayabusa2# (lander)
- Lucy (multiple flybys)
- DART (impactor)
| |
|---|
| Past | | Flybys | |
|---|
| Orbiters | |
|---|
| Landers |
- Hayabusa
- Hayabusa2
- MASCOT
- Rover-1A / HIBOU
- Rover-1B / OWL
- Rover-2†
- NEAR Shoemaker
- Philae
|
|---|
| Impactors | |
|---|
| Sample return | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Planned |
- NEA Scout (flyby, 2022)
- Psyche (orbiter, 2023)
- Janus (flyby, 2023)
- DESTINY+ (multiple flybys, 2024)
- Hera (orbiter, 2024)
- ZhengHe (multiple flybys and sample return, 2025)
- Comet Interceptor (flyby, 2029)
|
|---|
| Proposed |
- ASTER (orbiter, 2021)
- Athena (flyby of Pallas, 2022)
- Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (flyby, 2023)
- Interstellar Express (flybys, 2024)
- Centaurus (multiple flybys, 2026-2029)
- Chimera (orbiter, 2025)
- CORSAIR (sample return)
- HAMMER (nuclear impactor concept)
- MANTIS (multiple flybys)
- OKEANOS (multiple flybys and sample return, 2026)
- World Is Not Enough (spacecraft refueling concept)
- Interstellar (flyby, 2030-2042)
|
|---|
Cancelled or
not developed | |
|---|
| Related |
- Asteroid belt
- Asteroid capture
- Asteroid mining
- Colonization of asteroids
- Ceres
- Pluto
- Small Solar System bodies
- Near-Earth object
- Trans-Neptunian object
- Trojan
- Vesta
|
|---|
- Probes are listed in chronological order of launch. † indicates mission failures.
|
Japanese space program |
|---|
|
Astronomical
observation | | Completed | |
|---|
| In operation | |
|---|
| Failed | |
|---|
| Planned |
- ATHENA2
- EUVST
- HiZ-GUNDAM
- LiteBIRD
- Nano-JASMINE
- Small-JASMINE
- Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope1
- WSO-UV5
- XRISM1
|
|---|
| Canceled | |
|---|
|
|---|
Communications,
broadcasting and
navigation | | Completed |
- BS
- Kakehashi
- Kirari
- Kizuna
- Kodama
- MBSat
- N-STAR
- Sakura (1
- 2a
- 2b
- 3a
- 3b)
- Yuri
|
|---|
| In operation |
- Kirameki
- Michibiki
- MTSAT
- N-STAR
- JDRS
|
|---|
| Planned | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Earth observation | | Completed | |
|---|
| In operation | |
|---|
| Planned | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Engineering tests | | Completed | |
|---|
| In operation | |
|---|
| Planned |
- BEAK
- ETS-IX
- G-SATELLITE
- SERVIS-3
- Small Demonstration Satellite
|
|---|
| Canceled | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Human spaceflight | | Completed | |
|---|
| In operation | |
|---|
| Planned |
- H-II Transfer Vehicle
- Lunar Gateway1245
|
|---|
| Cancelled | |
|---|
|
|---|
Lunar and
planetary exploration | | Completed | |
|---|
| In operation |
- Akatsuki
- BepiColombo (MMO/Mio)2
- Hayabusa2
|
|---|
| Failed | |
|---|
| Planned |
- Comet Interceptor2
- DESTINY+
- EQUULEUS
- HERACLES24
- JUICE2
- LUPEX8
- MELOS
- MMX
- OMOTENASHI
- SLIM
- TEREX
|
|---|
| Cancelled | |
|---|
| Proposed | |
|---|
|
|---|
Private
miniaturized satellites | | Completed | |
|---|
| In operation | |
|---|
| Planned | |
|---|
|
|---|
| Reconnaissance | | Completed | |
|---|
| In operation | |
|---|
| Planned | |
|---|
|
|---|
- Italics indicates projects in development.
- Superscripts indicate joint development with1NASA, 2ESA, 3ASI, 4CSA, 5RKA, 6AEB, 7INPE and 8ISRO.
|
← 1984 · Orbital launches in 1985 · 1986 → |
|---|
Sakigake | Kosmos 1616 | Kosmos 1617 · Kosmos 1618 · Kosmos 1619 · Kosmos 1620 · Kosmos 1621 · Kosmos 1622 | Molniya-3 No.36 | Kosmos 1623 | Kosmos 1624 | Gorizont No.21L | Kosmos 1625 | Kosmos 1626 | STS-51-C (USA-8) | Kosmos 1627 | Kosmos 1628 | Meteor-2 No.13 | USA-9 | Arabsat-1A · Brasilsat A1 | Kosmos 1629 | Kosmos 1630 | Kosmos 1631 | Kosmos 1632 | Kosmos 1633 | Geosat | Kosmos 1634 | Kosmos 1635 · Kosmos 1636 · Kosmos 1637 · Kosmos 1638 · Kosmos 1639 · Kosmos 1640 · Kosmos 1641 · Kosmos 1642 | Ekran No.28L | Intelsat VA F-10 | Kosmos 1643 | Kosmos 1644 | STS-51-D (Anik C1 · Leasat 3) | Unnamed | Kosmos 1645 | Kosmos 1646 | Kosmos 1647 | Kosmos 1648 | Prognoz 10 | STS-51-B ( Nusat) | GStar-1 · Telecom 1B | Kosmos 1649 | Kosmos 1650 · Kosmos 1651 · Kosmos 1652 | Kosmos 1653 | Kosmos 1654 | Molniya-3 No.39 | Kosmos 1655 | Kosmos 1656 | Soyuz T-13 | Kosmos 1657 | Kosmos 1658 | Kosmos 1659 | Kosmos 1660 | STS-51-G ( Morelos 1 · Arabsat-1B · Telstar 3D · SPARTAN-101) | Kosmos 1661 | Kosmos 1662 | Progress 24 | Kosmos 1663 | Unnamed | Kosmos 1664 | Intelsat VA F-11 | Giotto | Kosmos 1665 | Kosmos 1666 | Kosmos 1667 | Kosmos 1668 | Molniya-3 No.37 | Kosmos 1669 | STS-51-F ( PDP) | Kosmos 1670 | Kosmos 1671 | Transit-O 24 · Transit-O 30 | Kosmos 1672 · Kosmos 1672 | Kosmos 1673 | Kosmos 1674 | Gran' No.26L | Kosmos 1675 | Kosmos 1676 | Suisei | Molniya-1 No.61 | Kosmos 1677 | STS-51-I (Aussat A1 · ASC-1 · Leasat 4) | Unnamed | Kosmos 1678 | Kosmos 1679 | Kosmos 1680 | Kosmos 1681 | ECS-3 · Spacenet 3 | Soyuz T-14 | Kosmos 1682 | Kosmos 1683 | Kosmos 1684 | Kosmos 1685 | Kosmos 1686 | Intelsat VA F-12 | Kosmos 1687 | Kosmos 1688 | Kosmos 1689 | Molniya-3 No.38 | STS-51-J (USA-11 · USA-12) | USA-10 | Kosmos 1690 · Kosmos 1695 · Kosmos 1692 · Kosmos 1693 · Kosmos 1694 · Kosmos 1691 | Kosmos 1696 | Fanhui Shi Weixing 8 | Kosmos 1697 | Kosmos 1698 | Molniya-1 No.73 | Unnamed | Meteor-3 No.2 | Kosmos 1699 | Kosmos 1700 | Molniya-1 No.56 | STS-61-A ( GLOMR) | Kosmos 1701 | Kosmos 1702 | Gran' No.28L | Kosmos 1703 | STS-61-B ( Morelos 2 · Aussat A2 · Satcom K2 · OEX · EASE/ACCESS) | Kosmos 1704 | Kosmos 1705 | Kosmos 1706 | Kosmos 1707 | USA-13 · USA-14 | Kosmos 1708 | Kosmos 1709 | Molniya-3 No.40 | Kosmos 1710 · Kosmos 1711 · Kosmos 1712 | Meteor-2 No.14 | Kosmos 1713 | Kosmos 1714 |
Payloads are separated by bullets ( · ), launches by pipes ( | ). Crewed flights are indicated in underline. Uncatalogued launch failures are listed in italics. Payloads deployed from other spacecraft are denoted in (brackets). |
На других языках
[de] Sakigake
Sakigake (jap. .mw-parser-output .Hira{font-size:120%}さきがけ, dt. „Vorbote“) war eine japanische Raumsonde, die 1985 zur Erforschung des Kometen Halley gestartet wurde. Sakigake kam bis auf 7.000.000 km an den Kometen heran, ihre Schwestersonde Suisei 151.000 km.
- [en] Sakigake
[es] Sakigake
La Sakigake (さ き が け, "pionero" o "precursor" en idioma japonés), identificada inicialmente como MS-T5, fue una sonda espacial japonesa lanzada el 7 de enero de 1985 a bordo de un cohete M-3SII-1, desde el Centro Espacial de Uchinoura. Su desarrollo y lanzamiento se llevó a cabo por el Instituto de Ciencia Aeronáutica y Espacial (ISAS), actualmente integrado en la JAXA.
[ru] Сакигакэ
Сакигакэ (яп. さきがけ, буквально «Пионер») — первая японская автоматическая межпланетная станция и первый межпланетный зонд, созданный не США и не СССР. Аппарат предназначался для демонстрации эффективности новой ракеты-носителя, испытания схем преодоления гравитационного притяжения Земли на базе японской техники, наблюдения космической плазмы и магнитного поля в межпланетном пространстве. Сакигакэ — часть так называемой «Армады Галлея», группы космических аппаратов отправленных на изучение кометы Галлея. Сигналы Сакигакэ позволили внести корректировки для аппарата Суйсэй, запущенного несколькими месяцами позже.
Текст в блоке "Читать" взят с сайта "Википедия" и доступен по лицензии Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike; в отдельных случаях могут действовать дополнительные условия.
Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
2019-2025
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии




