cosmos.wikisort.org - Spacecraft
Zond 2 was a Soviet space probe, a member of the Zond program, and was the sixth Soviet spacecraft to attempt a flyby of Mars.[1][2] (See Exploration of Mars)[3] It was launched on November 30, 1964 at 13:12 UTC onboard Molniya 8K78 launch vehicle from Baikonur Cosmodrome, Kazakhstan, USSR. The spacecraft was intended to survey Mars but lost communication before arrival.
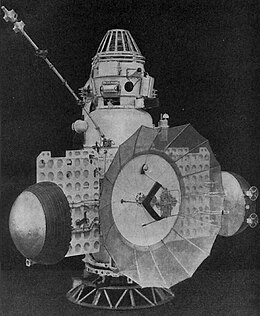 The Soviet Zond 2. | |
| Names | Zond 3MV-4 No. 2 |
|---|---|
| Mission type | Mars flyby |
| Operator | OKB-1 |
| COSPAR ID | 1964-078C |
| SATCAT no. | 00945 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Bus | 3MV-4 |
| Launch mass | 890 kg (1,960 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | November 30, 1964, 13:12 UTC |
| Rocket | Molniya T103-16 |
| Launch site | Baikonur LC-1/5 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Heliocentric |
| Eccentricity | 0.216 |
| Perihelion altitude | 0.98 AU |
| Aphelion altitude | 1.52 AU |
| Inclination | 6.4° |
| Period | 508 days |
| Velocity | 5.62 km/s |
| Flyby of Mars | |
| Closest approach | August 6, 1965 |
| Distance | 1,500 km (930 mi) |
Zond | |
History
Zond-2 carried a phototelevision camera of the same type later used to photograph the Moon on Zond 3. The camera system also included two ultraviolet spectrometers. As on Mars 1, an infrared spectrometer was installed to search for signs of methane on Mars.
Zond 2 also carried six PPTs that served as actuators of the attitude control system. They were the first PPTs used on a spacecraft. The PPT propulsion system was tested during 70 minutes.
Zond 2, a Mars 3MV-4A craft, was launched on November 30, 1964. During some maneuvering in early May 1965, communications were lost. Running on half power due to the loss of one of its solar panels, the spacecraft flew by Mars on August 6, 1965 at 5.62 km/s, 1,500 km away from the planet.
Scientific Instruments[4]
- Radiation Detector
- Charged Particle Detector
- Magnetometer
- Piezoelectric Detector
- Radio Telescope
- Nuclear Component of Cosmic-ray Experiment
- Ultraviolet and Roentgen Solar Radiation Experiment
- Imaging System
See also
- List of missions to Mars
- Chronology of Mars Missions
References
- "Chronology of Mars Missions (PDF)". ResearchGate. doi:10.13140/rg.2.2.29797.65768. Archived from the original on December 10, 2018.
- "Zond 2 Mars Flyby ~ Fornax Space Missions". Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved December 26, 2018.
- Zond-2: An early attempt to touch Mars
- "In Depth | Zond 2". Solar System Exploration: NASA Science. Retrieved December 26, 2018.
External links
| Preceded by Zond 1 |
Zond program (interplanetary) | Succeeded by Zond 3 |
На других языках
[de] Zond 2
Zond 2 ist der Name einer gescheiterten sowjetischen Marssonde, die am 10. November 1964 gestartet wurde. Die Sonde gelangte zunächst in einen 153 × 219 km hohen Erdorbit und danach auf eine lange stark gebogene Mars-Transferbahn, um die Relativgeschwindigkeit zu minimieren. Da sich eines der beiden Solarpaneele nicht entfaltete, stand der Sonde nur die Hälfte der zu erwarteten elektrischen Leistung zur Verfügung. Im Laufe der Zeit wurde der Kontakt mit Zond 2 immer problematischer und lückenhafter. Er brach am 2. Mai 1965 endgültig ab. Am 6. August 1965 flog sie unterschiedlichen Angaben zufolge in einer Entfernung von 1500 oder 650.000 km[1] am Mars vorbei.- [en] Zond 2
[es] Zond 2
La misión Zond 2 consistía en una sonda para investigar el planeta Marte, el medio interplanetario y probar nuevos sistemas con la nave. La sonda llevaba los mismos instrumentos que la sonda Venera.[ru] Зонд-2
«Зонд-2» — автоматическая межпланетная станция второго поколения программы «Марс» из серии 3МВ (М-64). Космический аппарат предназначался для передачи информации о межпланетном пространстве, проведения с пролётной траектории научных исследований, в том числе получения снимков, Марса и изучения космического пространства около планеты. Станция была разработана в ОКБ-1.Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии



