cosmos.wikisort.org - Spacecraft
Soyuz 4 (Russian: Союз 4, Union 4) was launched on 14 January 1969, carrying cosmonaut Vladimir Shatalov on his first flight. The aim of the mission was to dock with Soyuz 5, transfer two crew members from that spacecraft, and return to Earth. The previous Soyuz flight (Soyuz 3) was also a docking attempt but failed for various reasons.
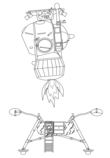
 Model of Soyuz 4 and Soyuz 5 after performing the first docking of two crewed spacecraft on 16 January 1969. | |
| Mission type | Test flight |
|---|---|
| Operator | Soviet space program |
| COSPAR ID | 1969-004A |
| SATCAT no. | 03654 |
| Mission duration | 2 days 23 hours 20 minutes 47 seconds |
| Orbits completed | 54 [1] |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft | Soyuz 7K-OK No.4 |
| Spacecraft type | Soyuz 7K-OK (active) |
| Manufacturer | Experimental Design Bureau (OKB-1) |
| Launch mass | 6625 kg |
| Landing mass | 2800 kg |
| Dimensions | 7.13 m long 2.72 m wide |
| Crew | |
| Crew size | 1 up 3 down |
| Members | Vladimir Shatalov |
| Landing | Vladimir Shatalov Aleksei Yeliseyev Yevgeny Khrunov |
| Callsign | Амур (Amur – "Amur River") |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 14 January 1969, 07:30:00 GMT |
| Rocket | Soyuz |
| Launch site | Baikonur, Site 31/6[2] |
| End of mission | |
| Landing date | 17 January 1969, 06:50:47 GMT |
| Landing site | 100 km at the southwest of Karaganda, Kazakhstan |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric orbit[3] |
| Regime | Low Earth orbit |
| Perigee altitude | 205.0 km |
| Apogee altitude | 223.0 km |
| Inclination | 51.73° |
| Period | 88.72 minutes |
| Docking with Soyuz 5 | |
| Docking date | 16 January 1969, 08:20 GMT |
| Undocking date | 16 January 1969, 12:55 GMT |
| Time docked | 4 hours 35 minutes |
Soyuz programme | |
The radio call sign of the crew was Amur, while Soyuz 5 was Baikal. This referred to the trans-Siberian railway project called the Baikal-Amur Mainline, which was in development at the time.
Crew
| Position | Launching Cosmonaut | Landing Cosmonaut |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | First spaceflight | |
| Flight Engineer | None | First spaceflight |
| Research Engineer | None | Only spaceflight |
Backup Crew
| Position | Launching Cosmonaut | Landing Cosmonaut |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | ||
| Flight Engineer | None | |
| Research Engineer | None | |
Reserve Crew
| Position | Launching Cosmonaut | Landing Cosmonaut |
|---|---|---|
| Commander | ||
| Flight Engineer | None | |
| Research Engineer | None | |
Mission parameters
- Mass: 6,625 kg (14,606 lb)
- Perigee: 205.0 km (127.4 mi) [3]
- Apogee: 223.0 km (138.6 mi)
- Inclination: 51.73°
- Period: 88.72 minutes
Space walk
- Yeliseyev and Khrunov – EVA 1
- EVA 1 start: 16 January 1969, 12:43:00 GMT
- EVA 1 end: 16 January 1969, 13:15:00 GMT
- Duration: 32 minutes
Mission highlights
The Soyuz 4 and 5 spacecraft docked on 16 January 1969, the first time two crewed spacecraft had docked (Apollo 9 would do the same in March of the same year). The two craft possessed only a primitive probe (Soyuz 4) and drogue (Soyuz 5) docking assembly. A connecting tunnel for the docking mechanism had not yet been developed, which prevented a simple internal transfer between the craft. This required the two transferring cosmonauts to spacewalk from one vehicle to the other. Aboard Soyuz 5, Yevgeny Khrunov and Aleksei Yeliseyev immediately began preparing for their extravehicular activity (EVA). Boris Volynov, who would remain aboard Soyuz 5, filmed them donning their Yastreb space suits.
On their 35th revolution of Earth, the two cosmonauts exited the spacecraft for the second Soviet spacewalk. One of Khrunov's lines became tangled and he accidentally closed the tumbler of his suit ventilator. This distracted Yeliseyev who did not set up the movie camera on the orbital module before exiting the spacecraft. As such, there is no film of the historic EVA, only a poor video transmission. One hour later, the two were greeted by Shatalov after the repressurisation of the Soyuz 4 orbital module, which also acted as an airlock. Soyuz 4 and 5 separated after 4 hours and 35 minutes docked together. Soyuz 4 re-entered the atmosphere and landed at 100 km (62 mi) at the southwest of Karaganda, in Kazakhstan, on 17 January 1969.
The mission proved it was possible to perform the activities that would be needed on a Soviet lunar landing. The Soviet plan called for a lone cosmonaut to land on the Moon, return to lunar orbit, then make a spacewalk back from the landing craft to the orbiting spacecraft after docking. This was because there was no internal tunnel between the two craft as found on the American Apollo CSM and LM.
The crew were to meet Leonid Brezhnev during a lavish ceremony at the Kremlin, but this was prevented by an attempted assassination of the Soviet leader. A man shot eight times at the motorcade but aimed at the car containing Georgy Beregovoy, Alexei Leonov, Andriyan Nikolayev, and Valentina Tereshkova. They were unharmed but Brezhnev's car was forced to speed away past the waiting Soyuz 4/5 crews on the podium.
EVA details
The docking mission had EVA objectives similar to those planned for Apollo 9. Soyuz 4 launched first, and was the active vehicle in the docking with Soyuz 5. The news agency TASS stated that: "there was a mutual mechanical coupling of the ships... and their electrical circuits were connected. Thus, the world's first experimental cosmic station with four compartments for the crew was assembled and began functioning". The mission rehearsed elements of the Soviet piloted lunar mission plan. Moscow TV carried the cosmonauts' EVA preparations live. Khrunov and Yeliseyev put on their Yastreb ("hawk") suits in the Soyuz 5 orbital module with aid from commander Boris Volynov.
Yastreb suit design commenced in 1965, shortly after Alexei Leonov's difficult EVA. Leonov served as a consultant for the design process, which was completed during 1966. Suit fabrication and testing occurred in 1967, but the fatal Soyuz 1 accident in April of that year and docking difficulties on the joint Soyuz 2-Soyuz 3 mission delayed its use in space until Soyuz 4-Soyuz 5.
To prevent the suit ballooning, the Yastreb suit featured a pulley-and-cable articulation system. Wide metal rings around the gray nylon canvas undersuit's upper arms served as anchors for the upper body articulation system. The Yastreb had a regenerative life support system in a rectangular white metal box placed on the chest and abdomen to facilitate movement through the Soyuz's hatchways.
Volynov checked out Khrunov and Yeliseyev's life support and communications systems before returning to the descent module, sealing the hatch, and depressurizing the orbital module. Khrunov went out first, transferring to the Soyuz 4 orbital module while the docked spacecraft were over South America, out of radio contact with the Soviet Union. Yeliseyev transferred while the spacecraft were over the Soviet Union. They closed the Soyuz 4 orbital module hatch behind them, then Soyuz 4 Commander Vladimir Shatalov repressurised the orbital module and entered to help Khrunov and Yeliseyev get out of their suits. The spacewalkers delivered newspapers, letters, and telegrams printed after Shatalov lifted off to help prove that the transfer took place.
See also
- List of spacewalks
References
- "Display: Soyuz 4 1969-004A". NASA. 14 May 2020. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Baikonur LC31". Encyclopedia Astronautica. Archived from the original on 4 September 2003. Retrieved 4 March 2009.
- "Trajectory: Soyuz 4 1969-004A". NASA. 14 May 2020. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
На других языках
- [en] Soyuz 4
[ru] Союз-4
«Союз-4» — пилотируемый космический корабль серии «Союз».Другой контент может иметь иную лицензию. Перед использованием материалов сайта WikiSort.org внимательно изучите правила лицензирования конкретных элементов наполнения сайта.
WikiSort.org - проект по пересортировке и дополнению контента Википедии